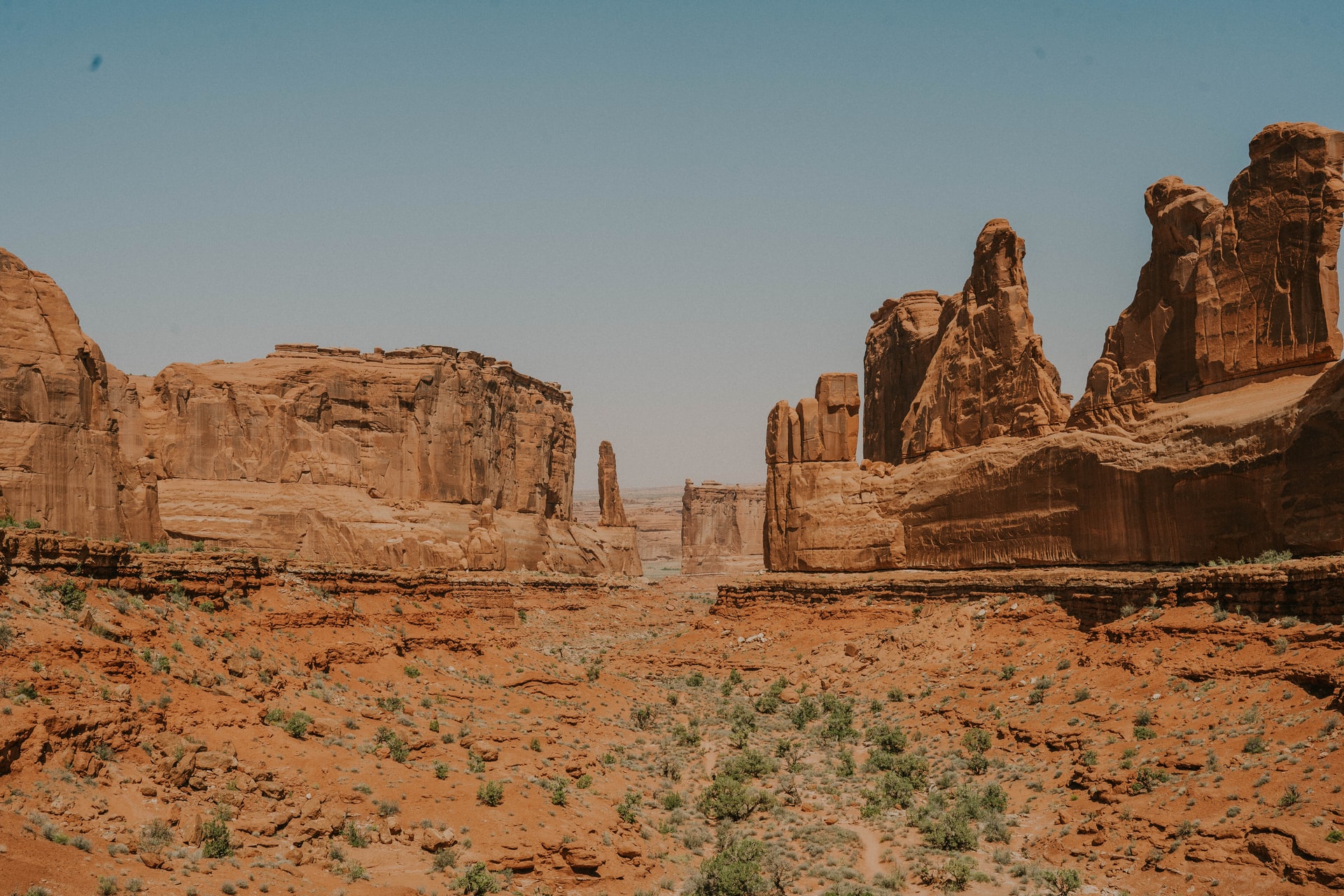
An important part of the non-living environment is the rocky shell, called the lithosphere. According to the scientific definition, the lithosphere is the Earth’s crust and the upper layer of the mantle, which are in a solid aggregate state. Beneath the lithosphere is the asthenosphere, a layer of mantle material that is characterized by increased plasticity and temperature readings capable of melting. The thickness and structure of the lithosphere are determined by the type of crust.
The lithosphere is broken by deep faults into large blocks – lithospheric plates, which, under the action of the Earth’s internal forces, move slowly.
The movement is carried out by two ways of oscillation:
- Horizontal. Moving across the viscous asthenosphere in one direction or another at a rate of up to 10-11 cm per year. This leads to the formation of large and linearly elongated landforms – mountains, oceanic depressions, rift ridges, and deep rifts on land – ridges.
- Vertical. Slow rises or falls at a rate of 0-2 to 10-12 mm per year. As a result of such movement, former seafloor areas become land or, conversely, land sinks to the bottom of the sea or ocean waters.